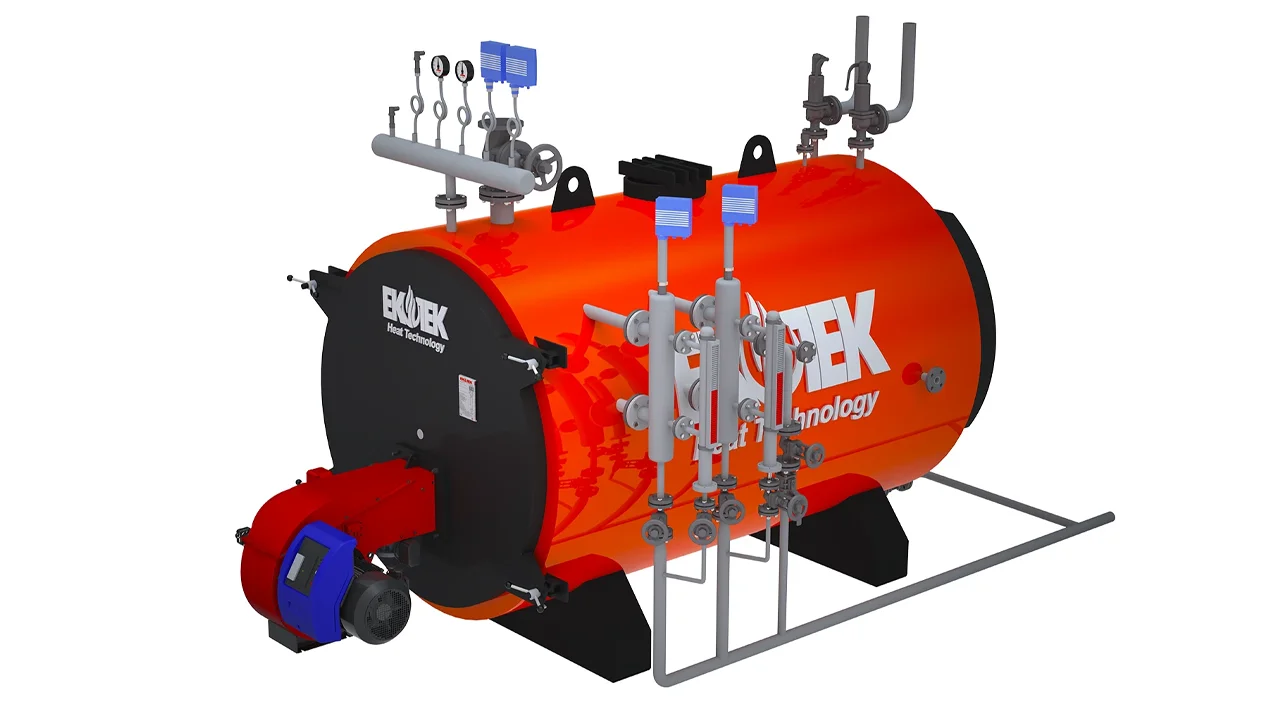
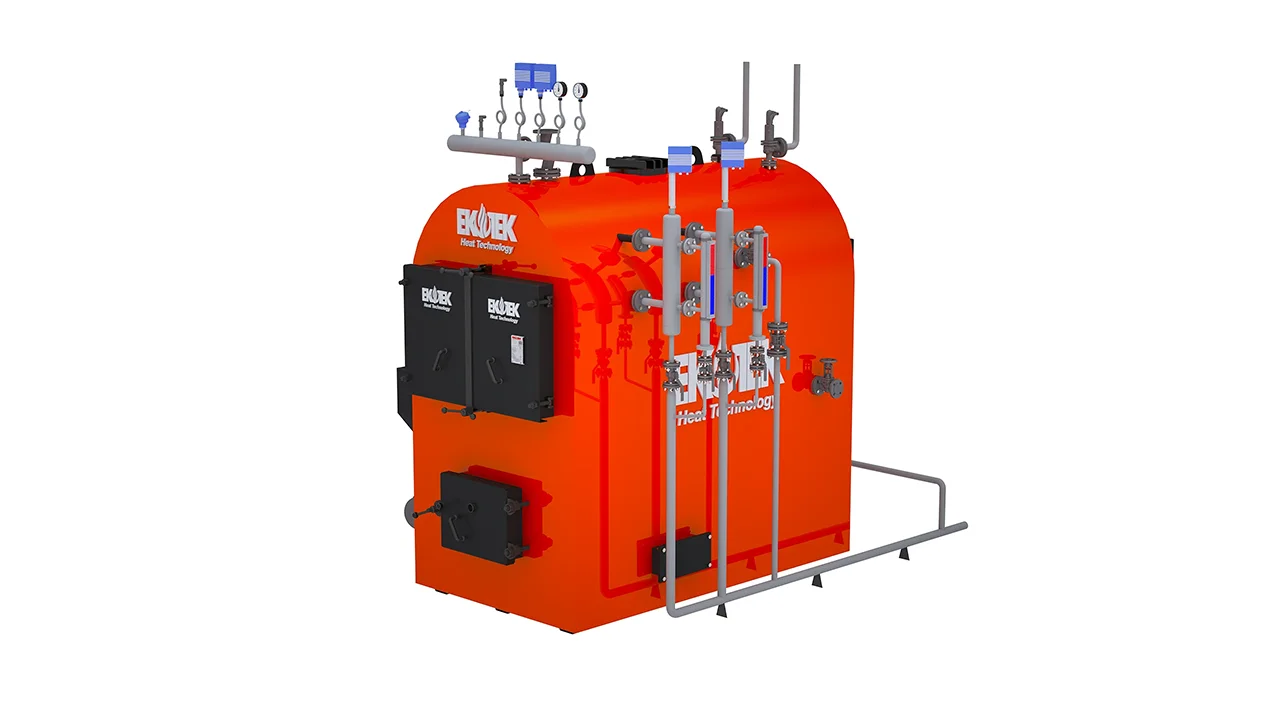
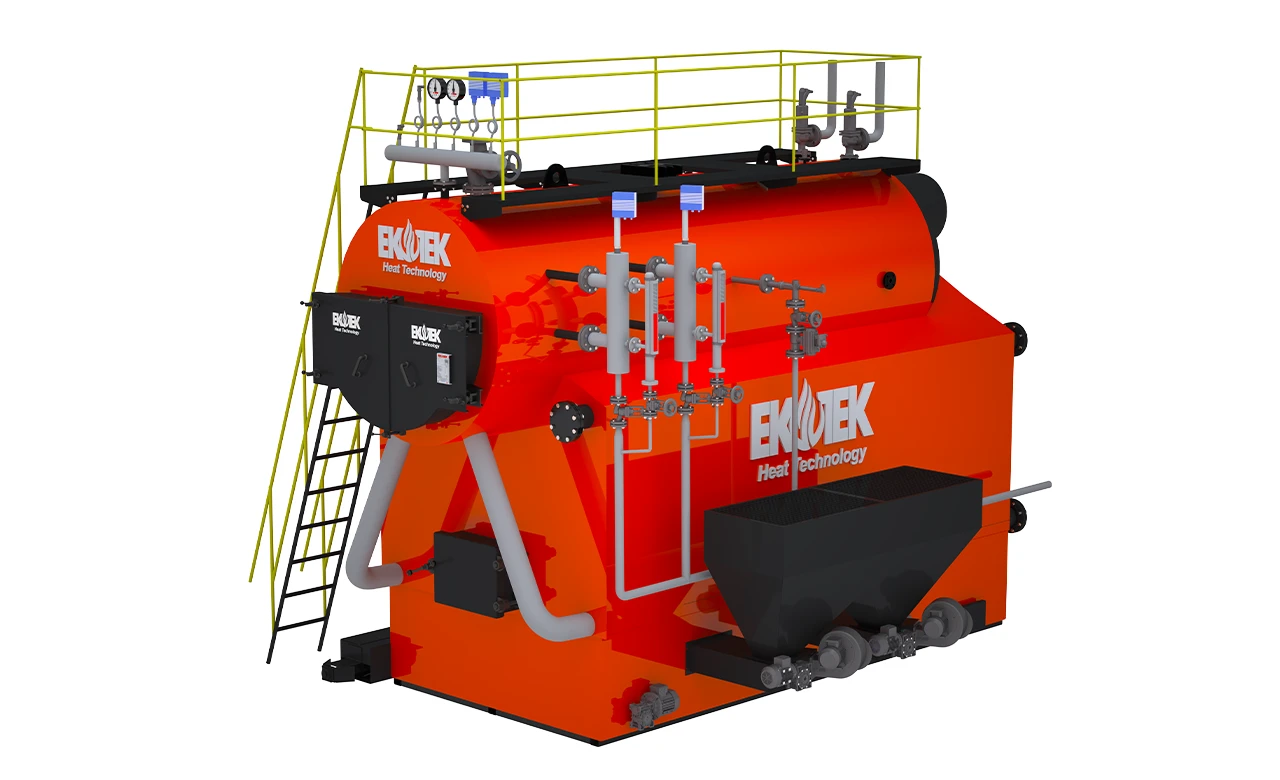
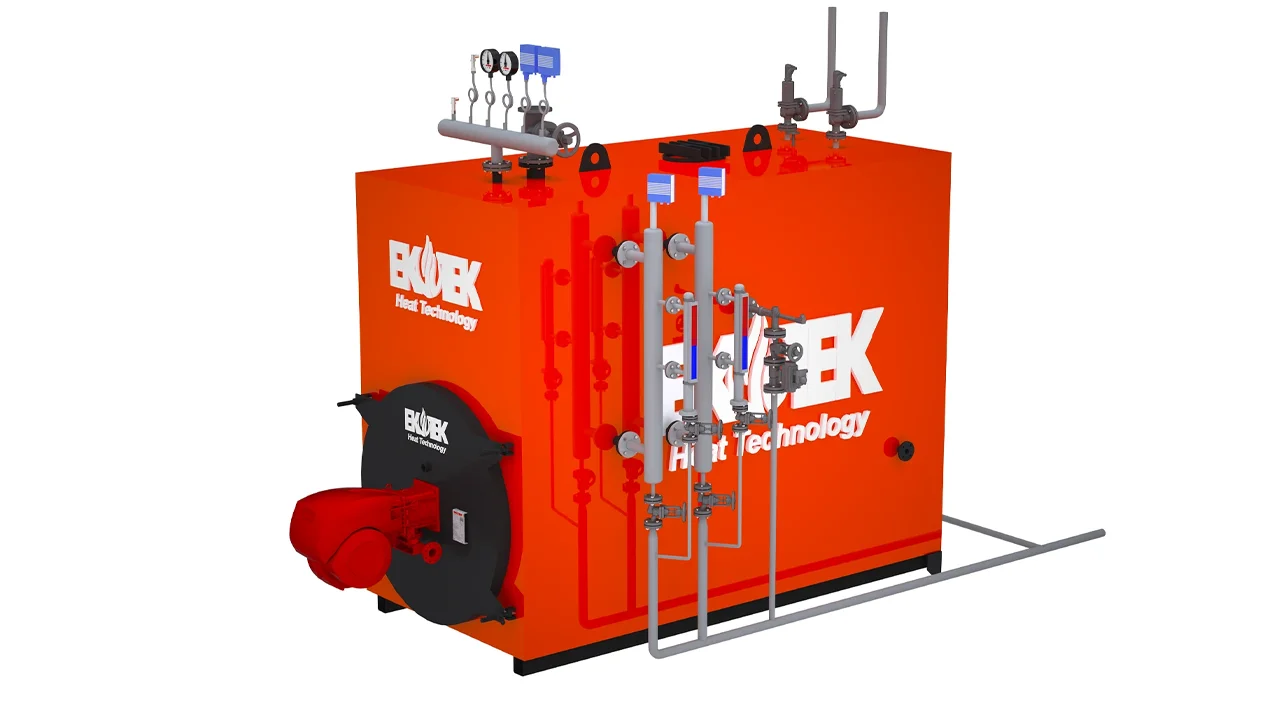
To illustrate this, consider how steam boilers operate.
Despite technological advances, the core principle remains straightforward: heat water to produce steam.
Here’s a step-by-step look at how the process unfolds:
-
Feedwater Supply
Treated water enters the boiler through the feedwater system. Good water quality prevents scaling and corrosion.
-
Heat Generation
The burner ignites fuel (such as natural gas, oil, biomass, or electricity) in the combustion chamber, producing heat.
-
Heat Transfer
Heat passes through metal tubes or surfaces, transferring energy to the surrounding water.
-
Steam Formation
At the boiling point, water vaporizes into steam, which collects in the steam drum.
-
Steam Distribution
Steam moves through pipes to process equipment, turbines, or heating systems.
-
Condensate Return
After releasing energy, the steam condenses back into water and returns to the boiler, forming a closed-loop system that conserves both water and energy.
This efficient cycle makes steam boilers a vital component in industrial heating and power systems.
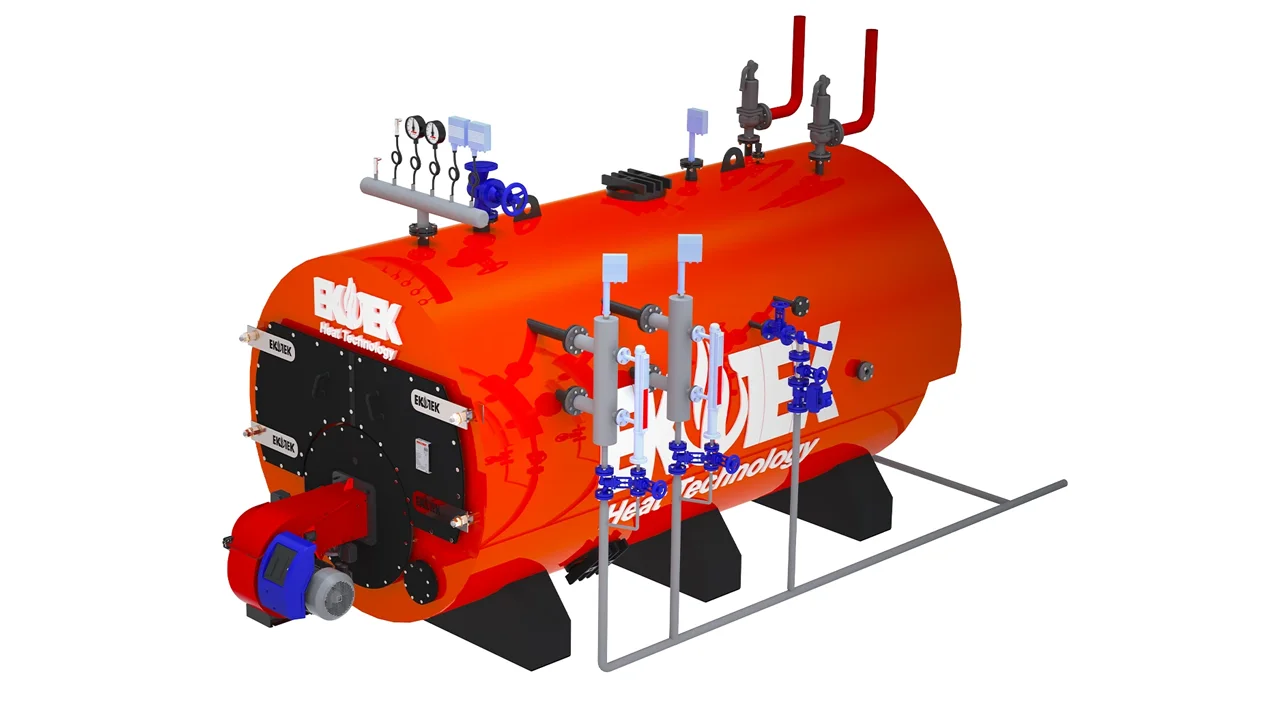
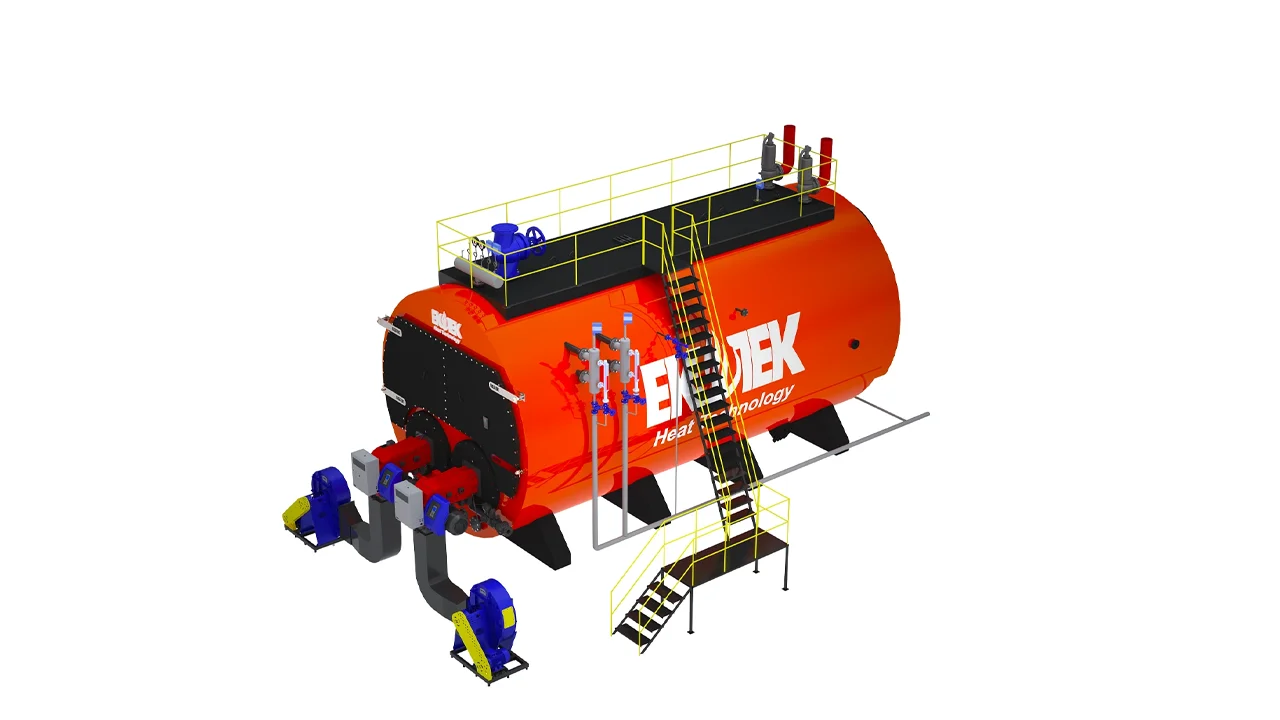
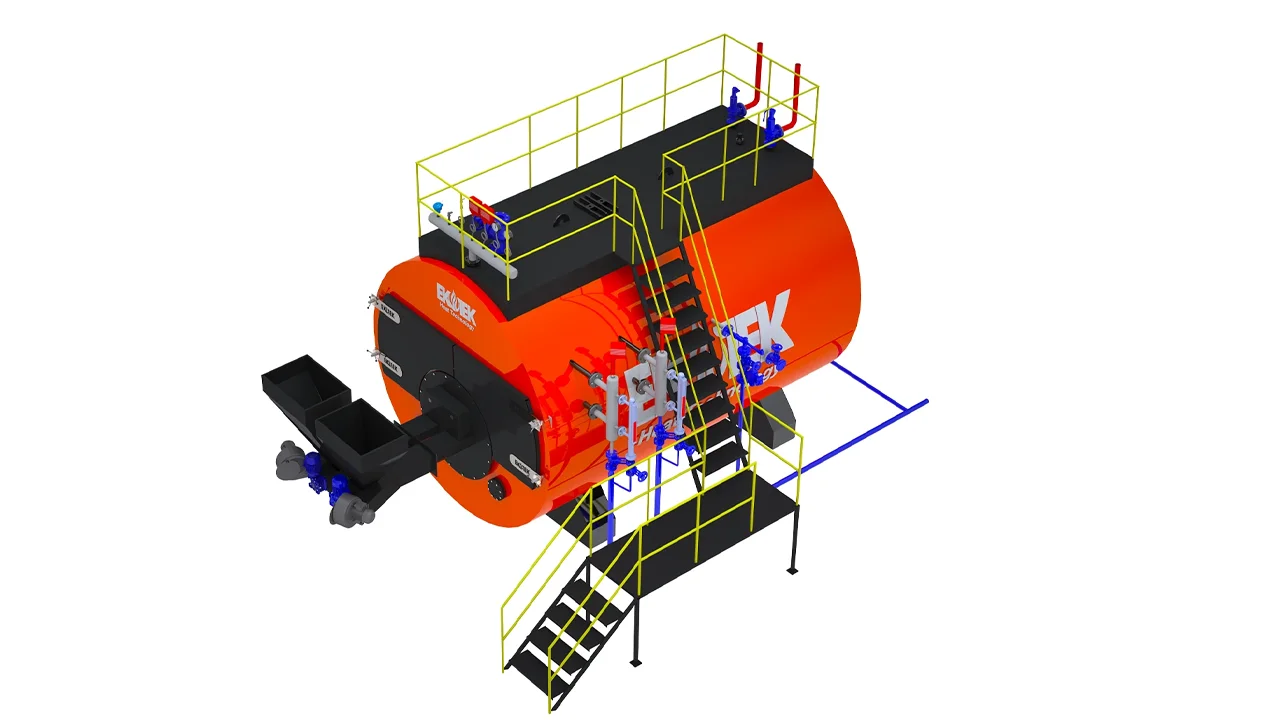
Major Components of a Steam Boiler
Each component plays a specific role in efficiency and safety:
|
Burner
|
Mixes fuel and air for efficient combustion.
|
|
Combustion Chamber
|
Contains the flame and transfers heat to the boiler water.
|
|
Heat Exchanger (Tubes)
|
Facilitates the transfer of heat from combustion gases to water.
|
|
Steam Drum
|
Collects and separates steam from water.
|
|
Feedwater System
|
Supplies water to maintain the proper level inside the boiler.
|
|
Safety Valves
|
Automatically release excess pressure to prevent accidents.
|
|
Control Panel
|
Monitors temperature, pressure, and safety functions automatically.
|
These components ensure steady steam production and minimize energy waste.
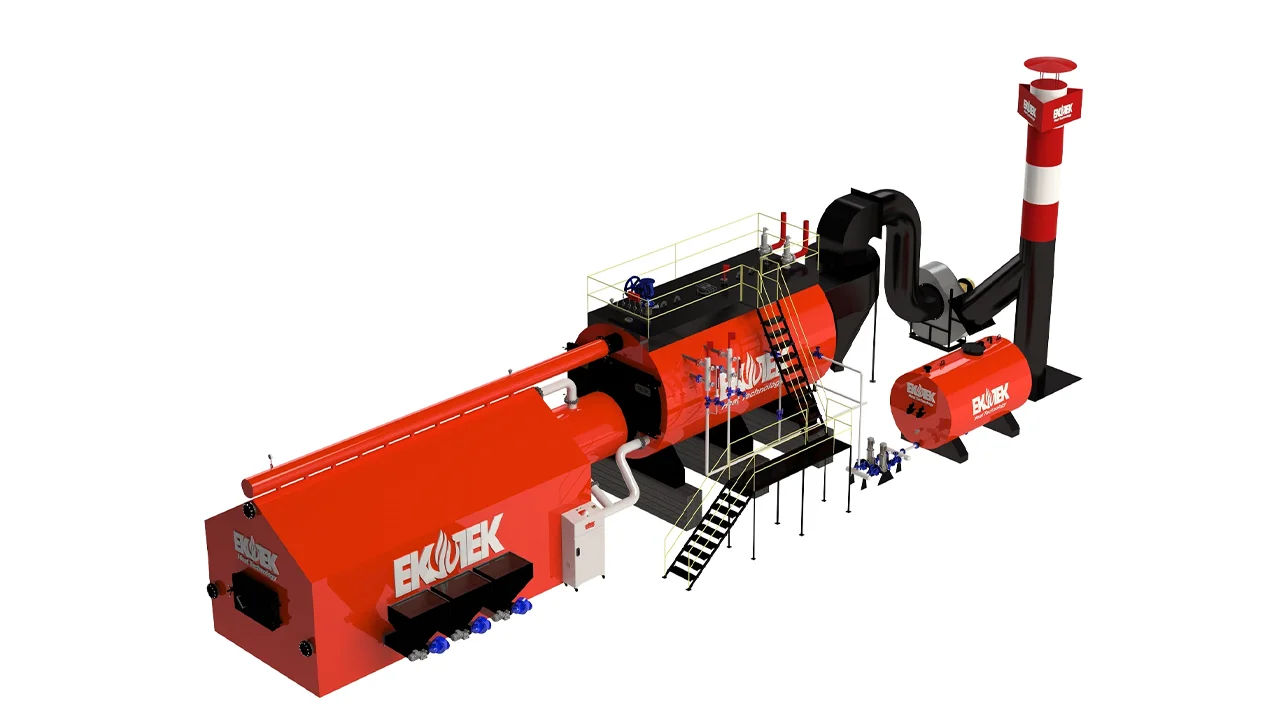
Types of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers are classified by design, fuel type, and intended use. Here are the most common types:
Fire-Tube Steam Boilers
In this design, hot gases travel through tubes surrounded by a cooling medium, typically water.
They are compact, easy to maintain, and suitable for low- to medium-pressure applications, such as heating or small factories.
Water-Tube Steam Boilers
Here, water flows inside tubes while combustion gases flow outside.
This design is capable of handling higher pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for use in power plants and other demanding industrial applications.
Electric Steam Boilers
Electric boilers use electricity. They are clean, quiet, low-maintenance, and produce zero on-site emissions. Many facilities choose them for their sustainability and space-saving.y and space-saving benefits.
Modular Steam Boilers
A modern approach uses multiple small, connected units.
This setup enables flexible operation, reduced downtime, and improved energy efficiency — ideal for industries with fluctuating steam demands.
Steam Boiler Efficiency Explained
Boiler efficiency measures how effectively fuel energy is converted into usable steam. Higher efficiency means lower fuel costs and emissions.
Factors Affecting Efficiency:
-
Proper air-fuel ratio
-
Regular maintenance and cleaning
-
Use of economizers to recover waste heat
-
Effective insulation to minimize heat loss
-
Correct water treatment to avoid scaling
Ekotek-style systems focus on on-demand steam generation and modular operation, allowing users to run only the needed boilers—reducing wasted energy.
Applications of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers serve numerous industries for both direct and indirect heating applications, such as the Food and beverage industry for sterilization, cooking, and packaging.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Steam sterilization of equipment and ingredients.
-
Textiles: Used for dyeing and drying.
-
Power Generation: Driving steam turbines to produce electricity.
-
Chemical plants: Provide heat for reactions.
-
Hospitals: Generating clean, reliable steam for sterilization and heating.
Their versatility makes them essential in industry and commerce.
Advantages of Steam Boilers
-
High Energy Transfer: Steam efficiently carries large amounts of heat energy.
-
Uniform Heating: Ideal for maintaining consistent temperatures.
-
Scalability: From small systems to large industrial units.
-
Fuel Flexibility: Works with natural gas, oil, or electricity.
-
Long Service Life: With proper maintenance, boilers can last decades.
-
Eco Options: New designs cut CO₂ and NOx emissions.
Maintenance and Safety Practices
Operating a steam boiler safely means regular attention and maintenance. Neglect risks energy loss, breakdowns, or accidents.
Essential Maintenance Tasks:
-
Daily checks on pressure, temperature, and water levels.
-
Regular blowdown to remove impurities.
-
Annual inspection of the combustion system and safety valves.
-
Routine testing of control systems and sensors.
Following a maintenance schedule ensures safety, efficiency, and reliability throughout a boiler’s life.
Modern Innovations in Steam Boiler Design
Today’s steam boilers are smarter, cleaner, and more efficient than ever before.
Innovations include On-Demand Steam, which produces steam only when needed.
-
IoT and Cloud Monitoring: Real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance.
-
Advanced Burner Controls: Optimize combustion for lower emissions.
-
Compact Modular Systems: Easy to install, scale, and maintain.
-
Electric & Hybrid Models: Designed for carbon-free operation.
These advances make modern boilers more sustainable and cost-effective, aligning with the global energy goals.