- Home
- Corporate
- Products
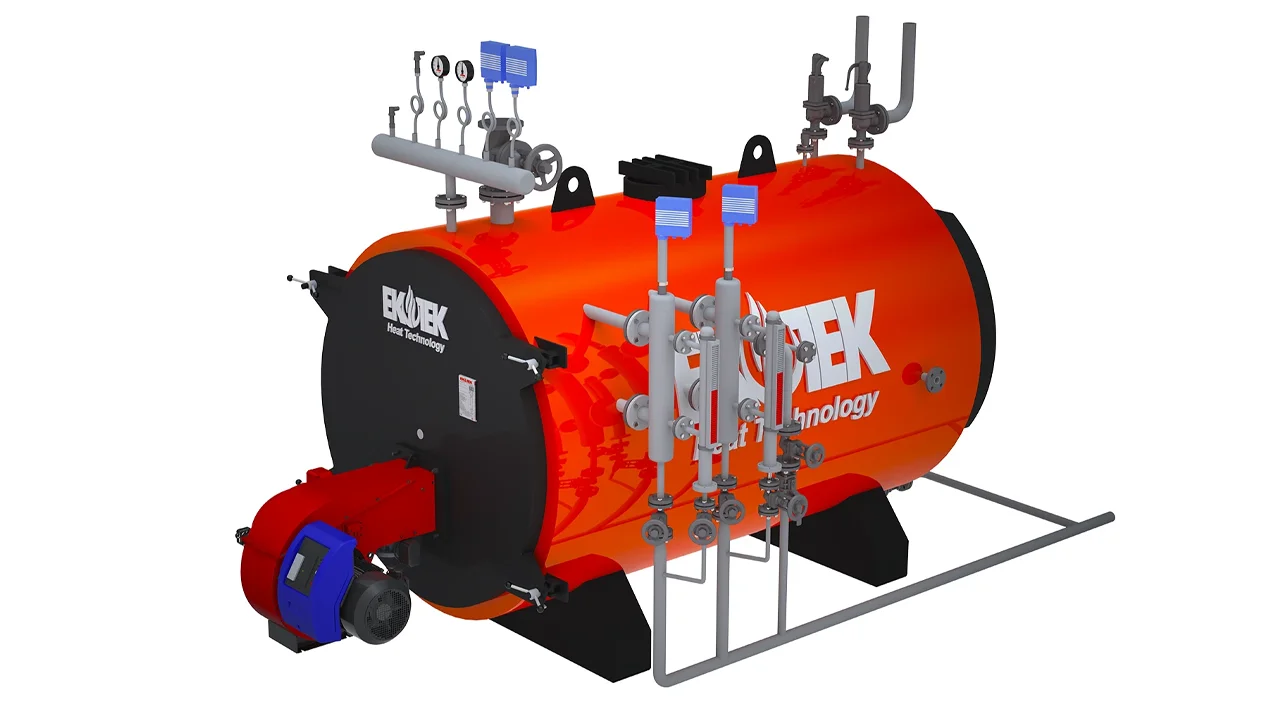
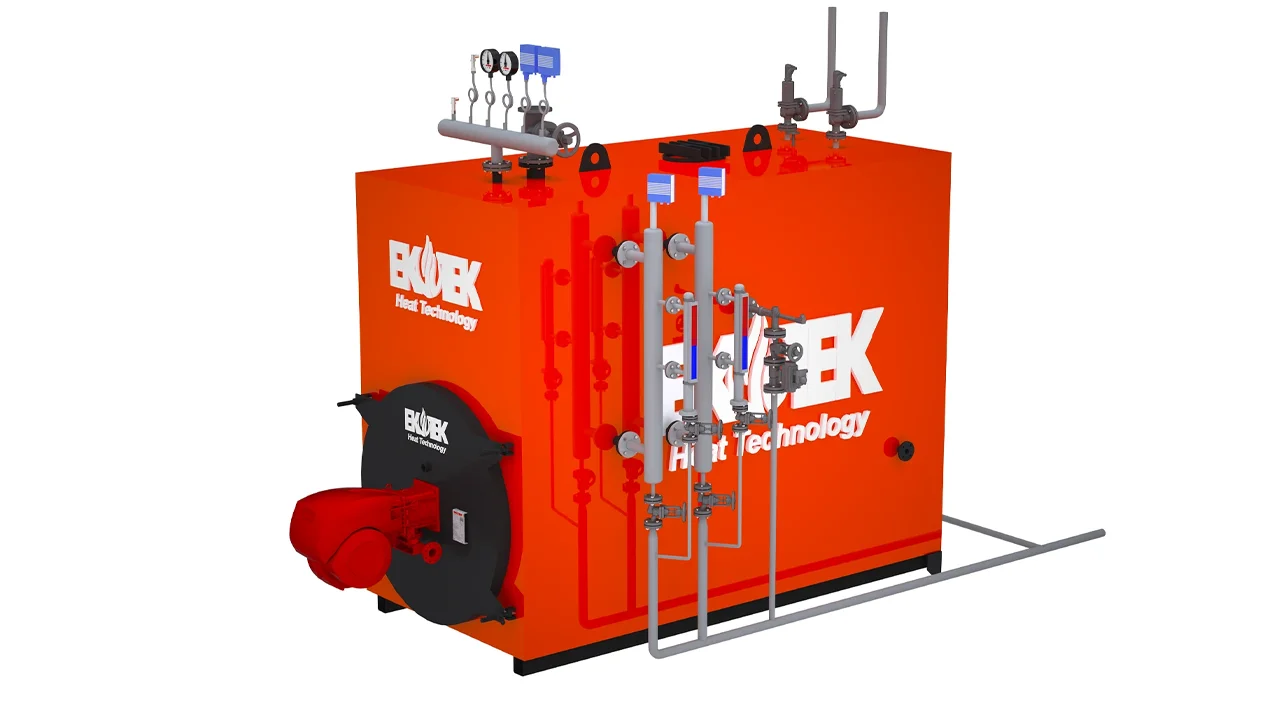
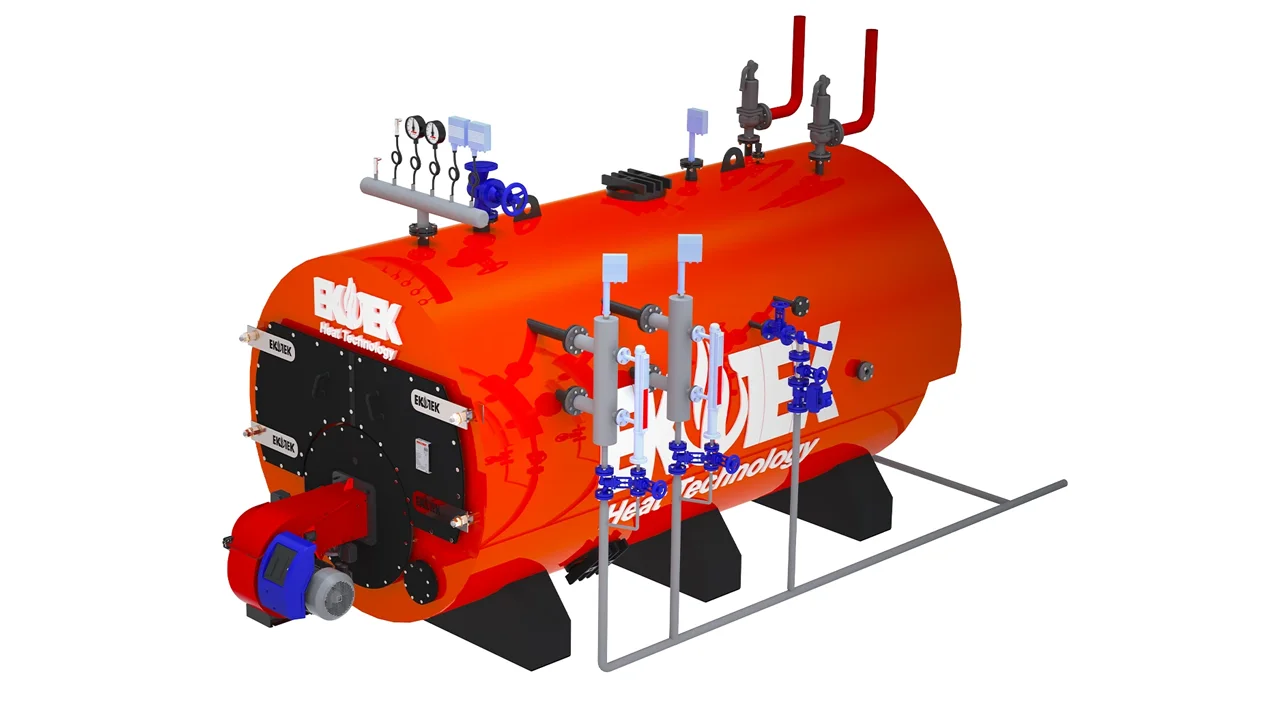
- Industrial Boilers
- Superheated Water Boiler
- Mobile Boiler Rooms
- Hot Air Boiler
- Central Heating Systems
- Residential Boilers
- Hot Water Boiler
- Pellet Boilers
- Custom Made Boilers
- Hot Water Storage Tank
- Tanks
- Condensate Tank
- Degasser Tank
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
- Accumulation Tank
- Economizer
- Accessories
- Media
- References
- After Sales
- Contact Us